Event-based vision
43 papers with code • 1 benchmarks • 9 datasets
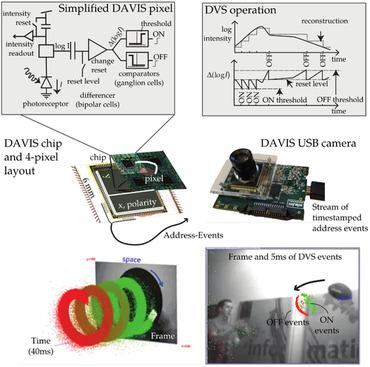
An event camera, also known as a neuromorphic camera, silicon retina or dynamic vision sensor, is an imaging sensor that responds to local changes in brightness. Event cameras do not capture images using a shutter as conventional cameras do. Instead, each pixel inside an event camera operates independently and asynchronously, reporting changes in brightness as they occur and staying silent otherwise. Modern event cameras have microsecond temporal resolution, 120 dB dynamic range, and less under/overexposure and motion blur than frame cameras.
Libraries
Use these libraries to find Event-based vision models and implementationsDatasets
Most implemented papers
Event-based Camera Pose Tracking using a Generative Event Model
Event-based vision sensors mimic the operation of biological retina and they represent a major paradigm shift from traditional cameras.
Event-based Background-Oriented Schlieren
Schlieren imaging is an optical technique to observe the flow of transparent media, such as air or water, without any particle seeding.
Detecting Every Object from Events
Object detection is critical in autonomous driving, and it is more practical yet challenging to localize objects of unknown categories: an endeavour known as Class-Agnostic Object Detection (CAOD).
Unsupervised Learning of a Hierarchical Spiking Neural Network for Optical Flow Estimation: From Events to Global Motion Perception
Convolutional layers with input synapses characterized by single and multiple transmission delays are employed for feature and local motion perception, respectively; while global motion selectivity emerges in a final fully-connected layer.
Focus Is All You Need: Loss Functions For Event-based Vision
The proposed loss functions allow bringing mature computer vision tools to the realm of event cameras.
Event-based Vision: A Survey
Event cameras offer attractive properties compared to traditional cameras: high temporal resolution (in the order of microseconds), very high dynamic range (140 dB vs. 60 dB), low power consumption, and high pixel bandwidth (on the order of kHz) resulting in reduced motion blur.
Event Cameras, Contrast Maximization and Reward Functions: An Analysis
The versatility of this approach has lead to a flurry of research in recent years, but no in-depth study of the reward chosen during optimization has yet been made.
A Tandem Learning Rule for Effective Training and Rapid Inference of Deep Spiking Neural Networks
Spiking neural networks (SNNs) represent the most prominent biologically inspired computing model for neuromorphic computing (NC) architectures.
A Large Scale Event-based Detection Dataset for Automotive
We introduce the first very large detection dataset for event cameras.
Lifting Monocular Events to 3D Human Poses
Here we propose the first learning-based method for 3D human pose from a single stream of events.
 CED
CED
 TUM-VIE
TUM-VIE
 N-ImageNet
N-ImageNet
 COESOT
COESOT
 Event-Human3.6m
Event-Human3.6m

